Constellation Tucana (Toucan)
Properties
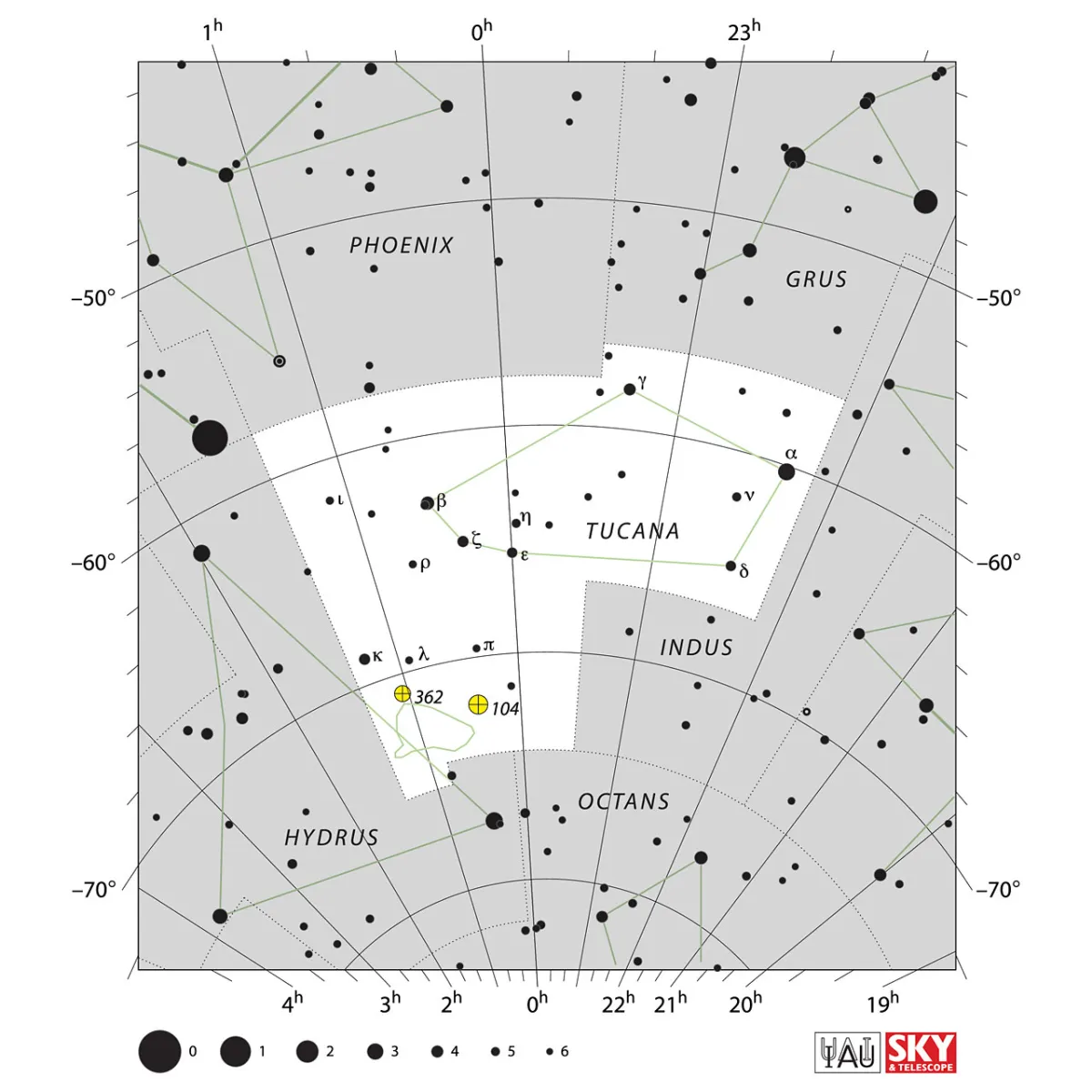
The constellation itself is relatively inconspicuous, but the toucan is easy to find because the Small Magellanic Cloud with the bright globular cluster 47 Tucanae is located in its southern part to the west like a blurred star. The area of this constellation is 295 square degrees and the centre culminates around midnight on September 17th. [9, 15]
| IAU Name | Tucana |
| IAU Genitive | Tucanae |
| IAU Abbr. | Tuc |
| English Name | Toucan |
| Culmination at local midnight | 21 September |
| Season (Latitude +0.0°) | May … February |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 22h 08m 27s … 01h 24m 49s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -75° 20' 50" … -56° 18' 46" |
| Area | 295 deg2 |
| Neighbours (N↻) | Phe, Gru, Ind, Oct, Hyi, Eri |
Deep-Sky Object Descriptions
Catalogues
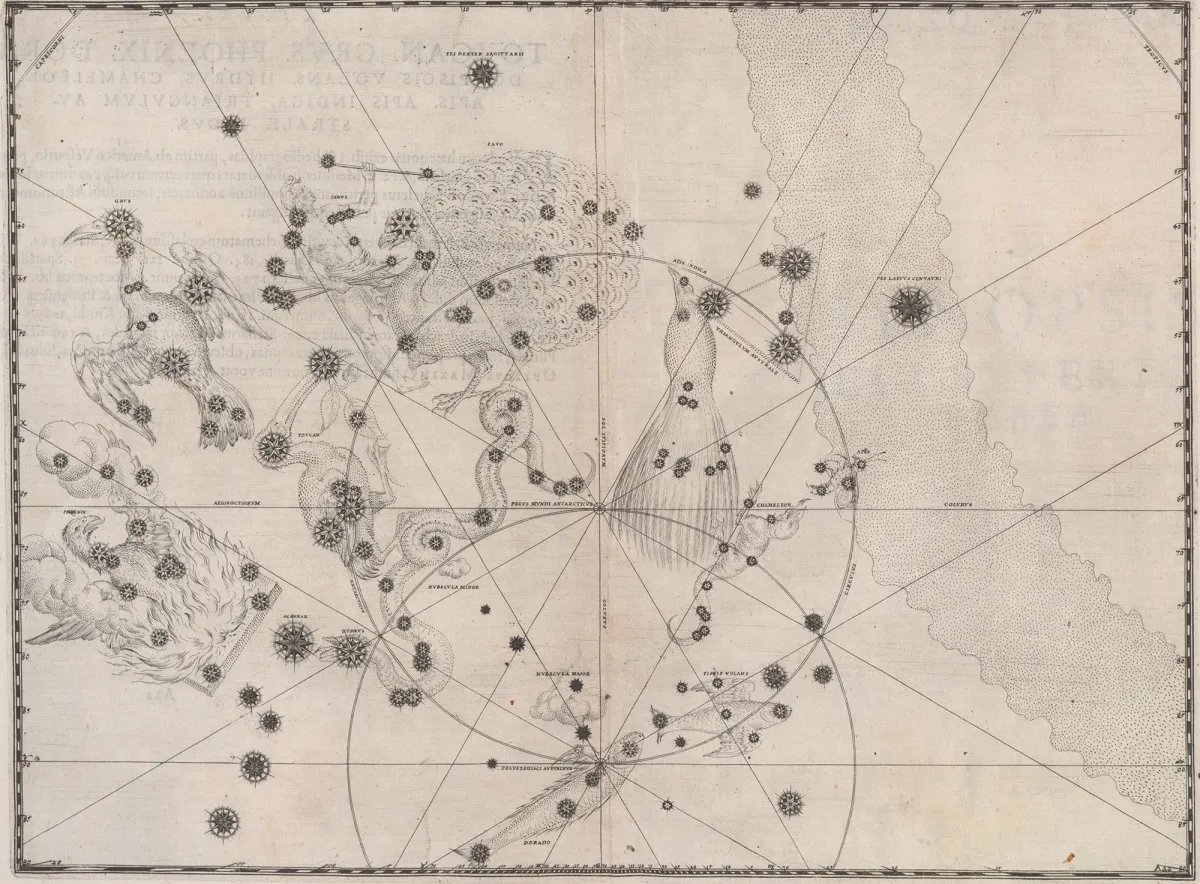
History
The constellation was introduced by Johann Bayer in 1603. It represents a toucan or pepper eater (Rhamphastidae), a bird native to the forest areas of Central and South America. These birds have a powerful, high and often very vividly coloured beak. [7]