Constellation Capricornus (Sea Goat)
Properties
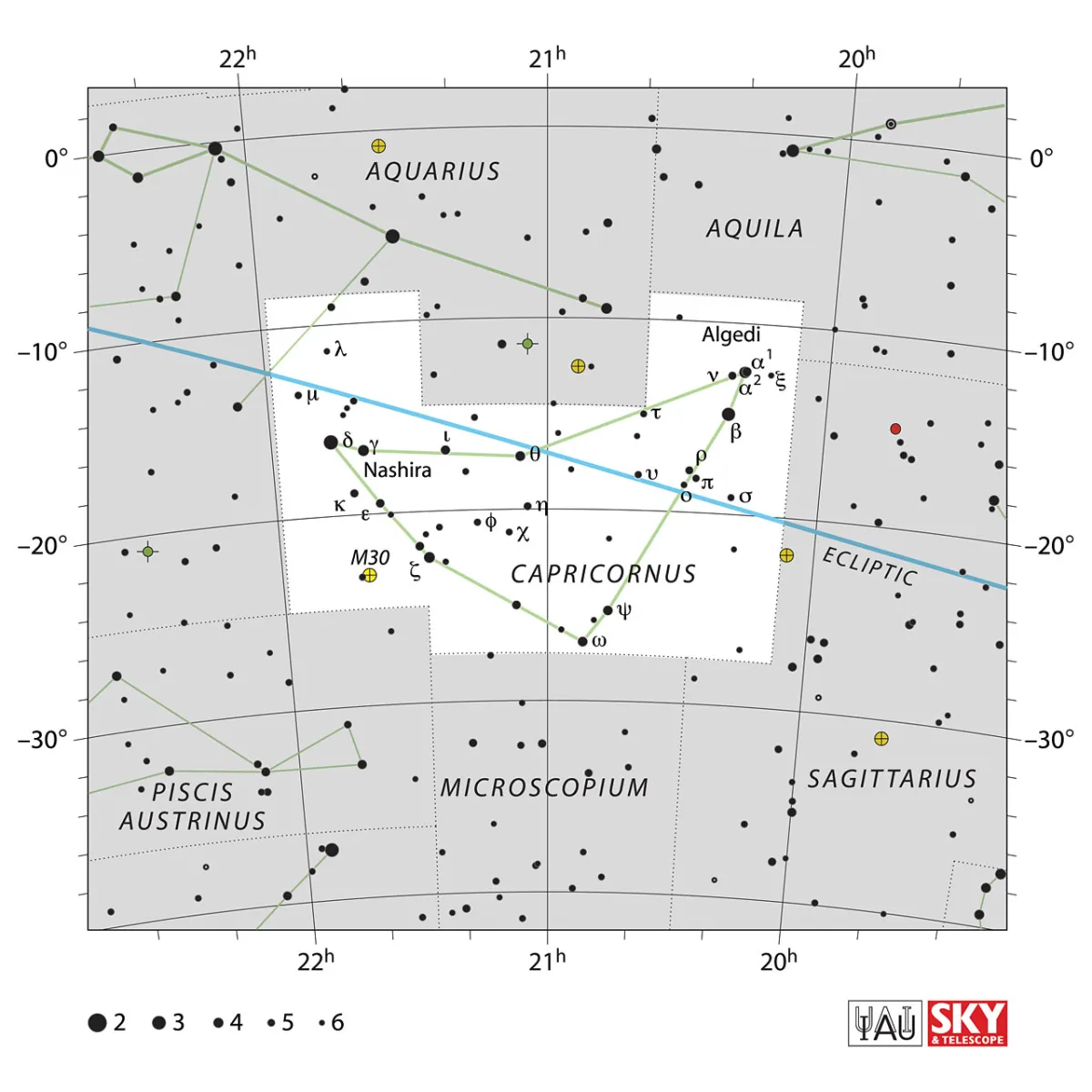
Capricornus is a less conspicuous constellation consisting mainly of stars of 4th and 5th magnitude. But it has the very distinctive shape of an arrow head pointing south. Capricornus is southeast of Aquila and east of Sagittarius. The area is 414 square degrees and the centre of the constellation culminates around midnight on August 5th. [9, 15]
| α1 Cap | Prima Giedi, Algiedi Prima, Algedi |
| α2 Cap | Secunda Giedi, Algiedi Secunda, Gredi, Algedi |
| β Cap | Dabih |
| γ Cap | Nashira |
| δ Cap | Deneb Algedi, Deneb Algiedi, Scheddi, Sheddi |
| ν Cap | Alshat |
| IAU Name | Capricornus |
| IAU Genitive | Capricorni |
| IAU Abbr. | Cap |
| English Name | Sea Goat |
| Culmination at local midnight | 5 August |
| Season (Latitude +0.0°) | April … January |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 20h 06m 46s … 21h 59m 05s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -27° 38' 31" … -08° 24' 16" |
| Area | 414 deg2 |
| Neighbours (N↻) | Aql, Sgr, Mic, PsA, Aqr |
Deep-Sky Object Descriptions
Catalogues
Mythology and History
Capricornus is often seen depicted with the head and torso of a goat and the tail of a fish. This unusual creature has been known for a long time and appears in numerous cultures. His image was found on stones from ancient Mesopotamia, today's Iraq. The Sumerian name for this constellation means goat fish.

In Greek mythology, Capricornus was associated with Pan, the boy of the gods. One day Pan met a group of pretty nymphs and goddesses who were laughing and playing in a field. To impress them, he turned into a goat and dived with one mighty leap into a nearby stream. The lower part of his body then turned into a fish tail. The king of the gods, Zeus - not averse to playing antics himself - was so amused by this caper that he took the goat fish to the starry sky. [81]
According to another legend, Pan is said to have turned into an ibex to hide from the giant Typhon. [10]
The Latin name Capricornus, which literally means goat's horn, is reminiscent of the story we find in the carter and which is about Amaltheia. It is not known exactly whether Amaltheia was the nymph herself or Amaltheia the goat belonging to the nymph. In any case, Zeus was suckled by this goat as a child before the time, and nectar and ambrosia flowed from the goat's horns. Ovid relates that one of these horns broke off and the nymphs filled it with fruit for Zeus. So it became a cornu copiae, a cornucopia, a symbol of abundance. Zeus later moved the goat to heaven out of gratitude. The goat star Capella reminds of this, but so does the goat horn Capricornus. [20]