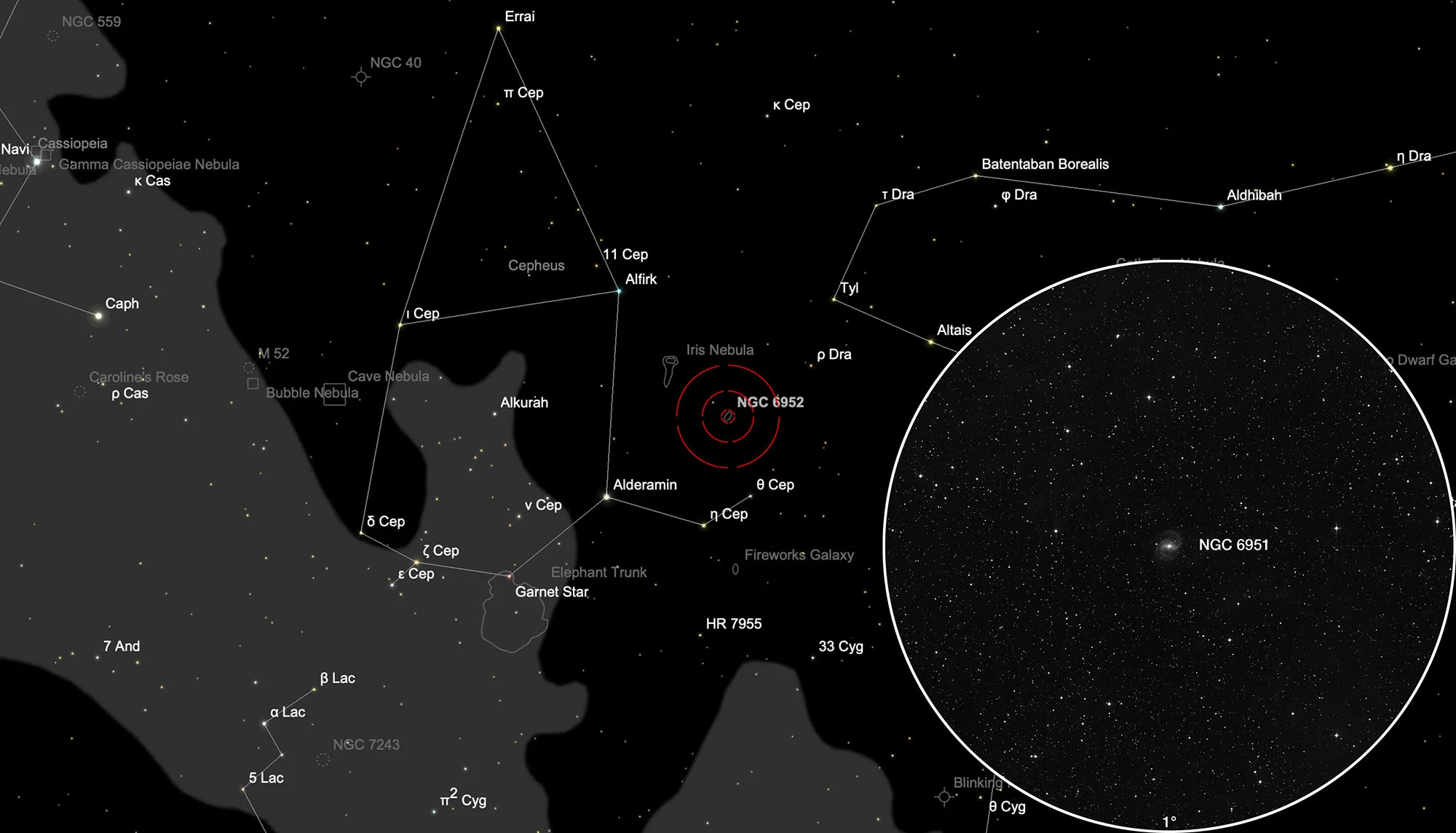
Galaxy NGC 6951 & Integrated Flux Nebula


History
In 1877 the French astronomer Jerome Eugene Coggia pointed the 7.2 inch f/11.5 comet finder refractor of the observatory in Marseille to the constellation Cepheus and discovered a nebula which he described as «fairly bright, oval, diffuse, star 15th magnitude east». Unfortunately he had gotten its position wrong by 20 arc minutes too far north. The following year, the American astronomer Lewis Swift encountered the same nebula with his 4.5 inch refractor, which he described as «fairly bright, fairly large, somewhat elongated» and whose position was correct measured The different positions led to John L. E. Dreyer listing Coggia's discovery as NGC 6952 and Swift's as NGC 6951 in his 1888 «New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars» [313]. Already in the appendix of the first «Index Catalogue» [314], published in 1895, reference was made to the double entry following a reference by William Denning. In the appendix to the «Second Index Catalogue» [315] published in 1910, the position of NGC 6951 was stated to be correct and that NGC 6952 should be deleted. [196, 277]
Physical Properties
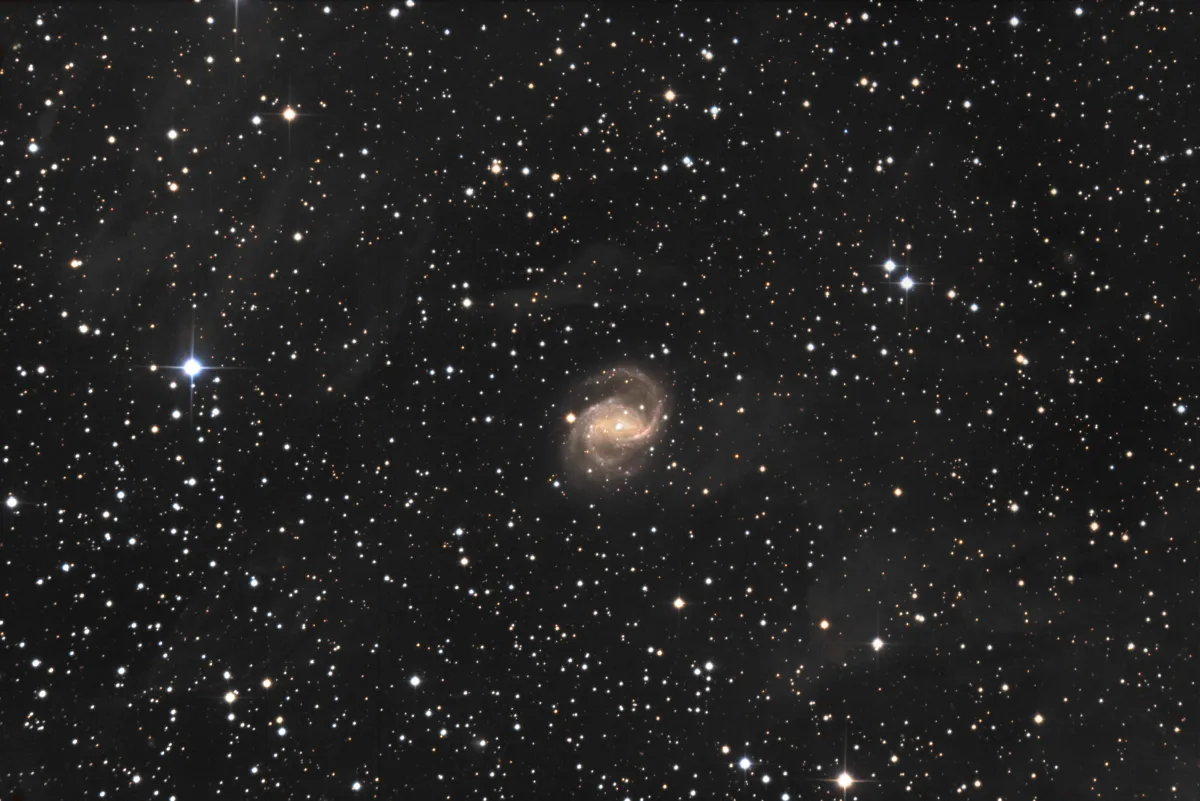
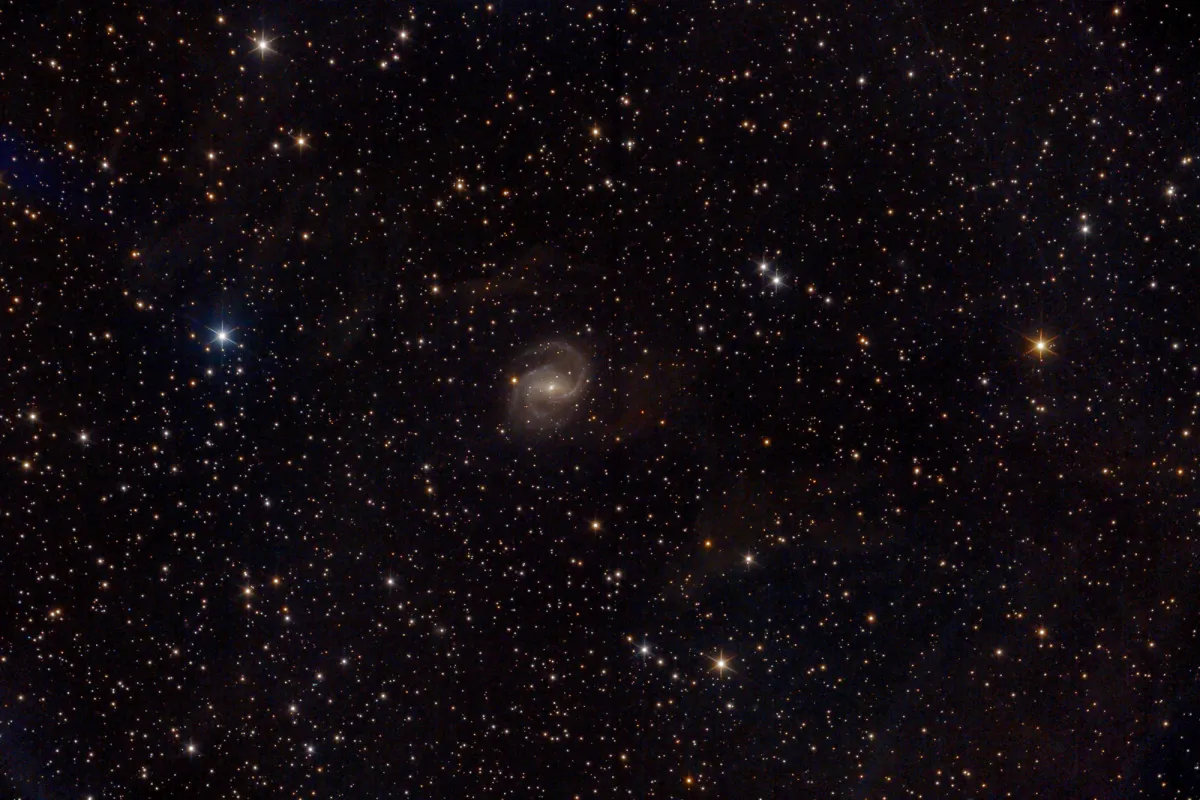
NGC 6951 is a Seyfert 2 galaxy with an active core and morphological type SAB(rs)bc. The distance is given as 16 to 24 Mpc. [145]
Long exposure images like Fig. 1 show nebulae that are in line of sight in front of the galaxy. These are large-scale gas and dust nebulae, so-called Integrated Flux Nebula (IFN), first discovered in 2005 by amateur astronomer Steve Mandel. Unlike the usual nebulae, these are located outside the plane of our Milky Way and are not illuminated by a single star, but by the sum of all stars in the Milky Way and shine very weakly. [271]
| Name | RA | Dec | Type | bMag | vMag | B-V | SB | Dim | PA | z | D(z) | MD | Dreyer Description | Identification, Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGC 6951 | 20 37 14.0 | +66 06 21 | dup | 11.6 | 10.7 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 3.9 × 3.2 | 170 | 0.004750 | 20.06 | 22.830 | pB, pL, lE | NGC 6952; UGC 11604; MCG 11-25-2; CGCG 325-3; IRAS 20366+6555 |
| NGC 6952 | 20 37 14.0 | +66 06 21 | Gx (SBbc) | 11.6 | 10.7 | 0.9 | 13.3 | 3.9 × 3.2 | 170 | 0.004750 | 20.06 | 22.830 | pB, oval, dif, * 15 close f | GC 6250; NGC 6951; UGC 11604; MCG 11-25-2; CGCG 325-3; IRAS 20366+6555 |
Finder Chart
The galaxy NGC 6951 is located in the constellation of Cepheus. On 31 July it is in opposition to the Sun and crosses the meridian at local midnight. The best observation time is April to December.