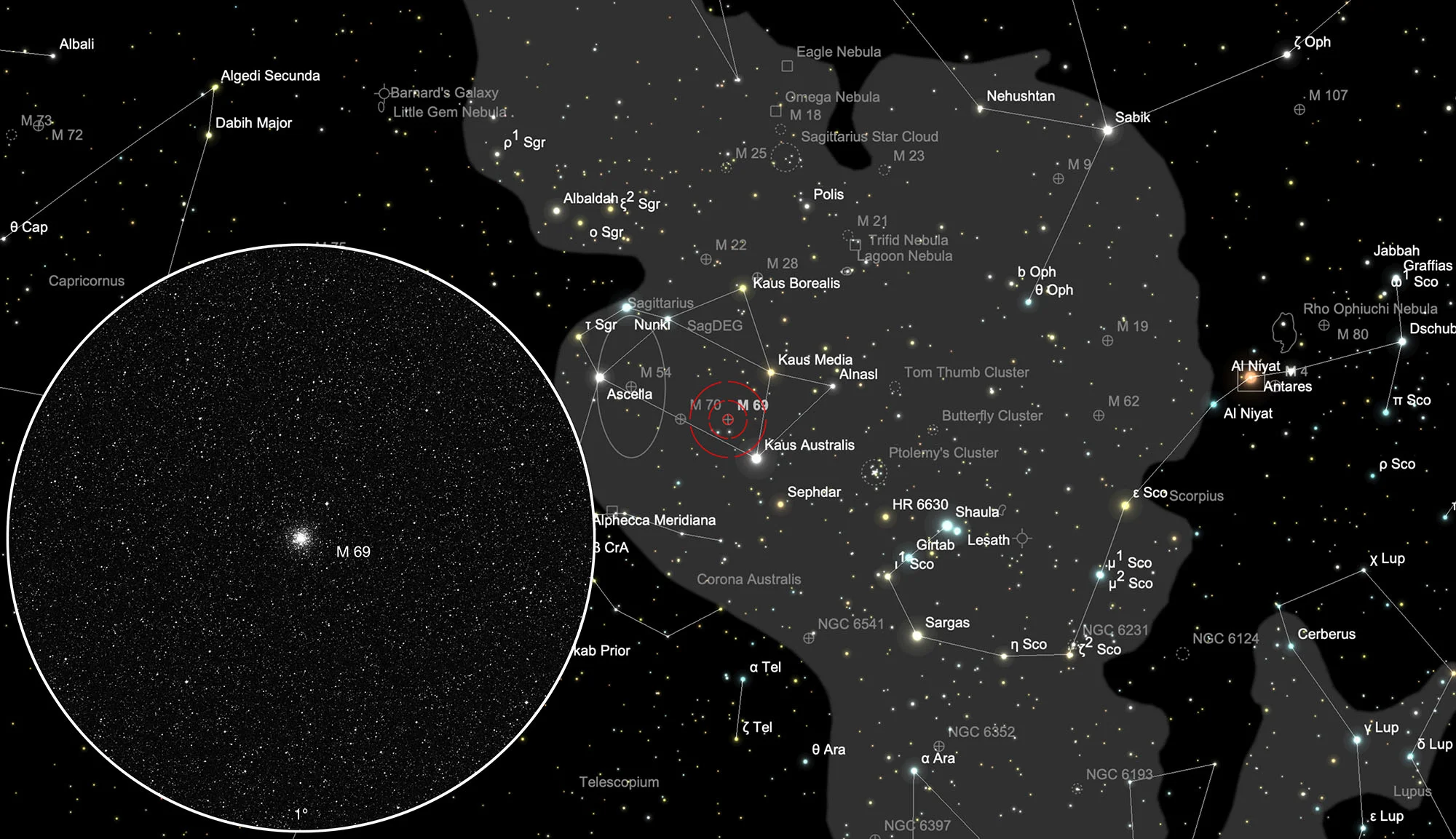
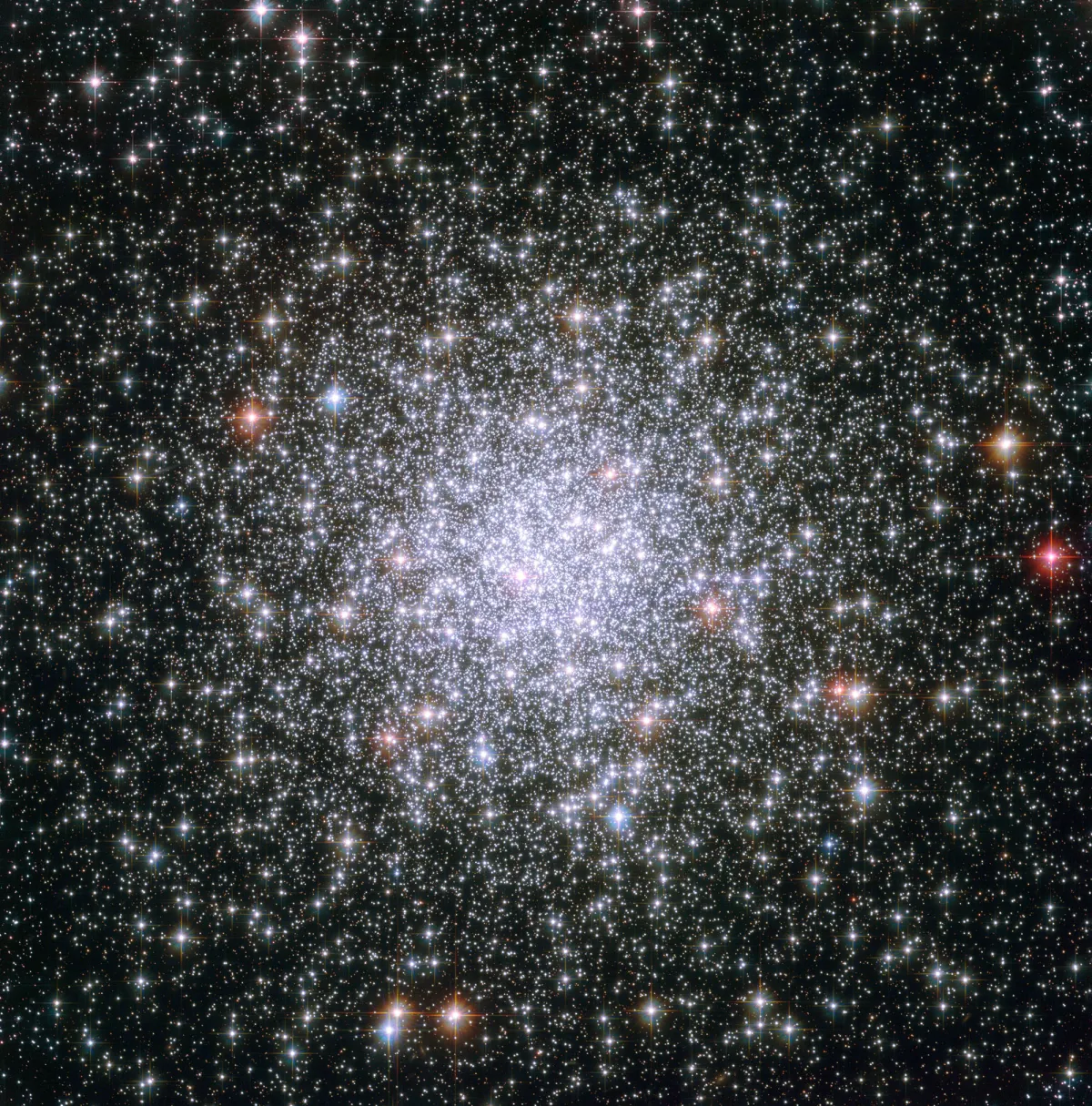
Globular Cluster Messier 69

History
This small globular cluster was discovered in 1752 by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille at the Cape of Good Hope. Through his small lens telescope, he described it as the «small nucleus of a comet» and could not break it down into individual stars. Charles Messier observed the 69th nebula of his catalog on 31 August 1780 and wrote: «Nebula without a star in Sagittarius, below his left arm and next to the bow; right next to it is a 9th magnitude star: it can only be seen in good weather, and the slightest light to illuminate the micrometer wires makes it disappear: the position was determined by ε of Sagittarius: this nebula was made by M. de la Cacaille observed and mentioned in its catalog; it would look like the nucleus of a small comet.» [4, 281]
Physical Properties
M 69 is one of the most metal-rich globular clusters, more than ten times that in globular clusters of a comparable age. By the way, in astronomy all elements are called metals, which are heavier than the two most common elements hydrogen. The nuclear fusion inside the stars produced elements occurring in nature up to and including iron. New stars arise from the remains of their predecessors, which is why the old globular clusters usually have a much smaller amount of metal than younger stars like our sun. M 69 is about 29'700 light years away from Earth. [215]
| Designation | NGC 6637 |
| Type | GCL (V) |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 18h 31m 23.2s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -32° 20' 51" |
| Diameter | 7.1 arcmin |
| Photographic (blue) magnitude | 9.3 mag |
| Visual magnitude | 8.3 mag |
| Metric Distance | 8.800 kpc |
| Dreyer Description | globular, B, L, R, rrr, st 14…16 |
| Identification, Remarks | h 3747; GC 4411; M 69; GCL 69; ESO 457-SC14 |
Finder Chart
M 69 is located in the constellation Sagittarius within the constellation known as "Teapot". Once you have M 69 in your field of view and seen enough, you switch off the tracking of the telescope. After 12 minutes there is already M 70, which is practically at the same declination. In the months of February to December, Sagittarius is highest above the southern horizon at night.