Planetary Nebula Abell 59

History
The planetary nebula Abell 59 was discovered in 1955 by the American astronomer George Ogden Abell on the photo plates of the Palomar Observatory Sky Survey (POSS). In 1955 he published a first list of 13 globular clusters and the positions of 73 planetary nebulae. The PN was then listed as number 48 (A55 48). In 1966 Abell published a completed list including the size and description of the 86 planetary nebulae discovered on the POSS photo plates. The PN was then listed as nebula 59 (A66 59). He described it with «e» as «a ring with gaps or incomplete ring». [331, 332]
The designation PK 53+3.1 originates from the two Czechoslovak astronomers Luboš Perek and Luboš Kohoutek, who in 1967 compiled a catalog of all the planetary nebulae of the Milky Way known at the time. [146]
The lesser known designation ARO 84 originates from 1971 survey of microwave radiation from planetary nebulae conducted by Canadian radioastronomer Lloyd A. Higgs using the 46-metre Algonquin Radio Observatory in Ontario, Canada. [136, 137]
Physical Properties
SkySafari 6 listfor the PN an apparent brightness of 16.39 mag an. On Simbad any magnitudes are missing. But one can find a distance of 1.4 kpc. [145, 149]
| Designations | PN G053.3+03.0: A 59, PK 53+03.1, A55 48, ARO 84, VV' 494 |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 19h 18m 41s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | +19° 33' 56" |
| Dimensions | 87." (optical), 75." (radio) |
| C-Star Magnitude | B: 22.21, V: 21.15 |
| Discoverer | ABELL 1955 |
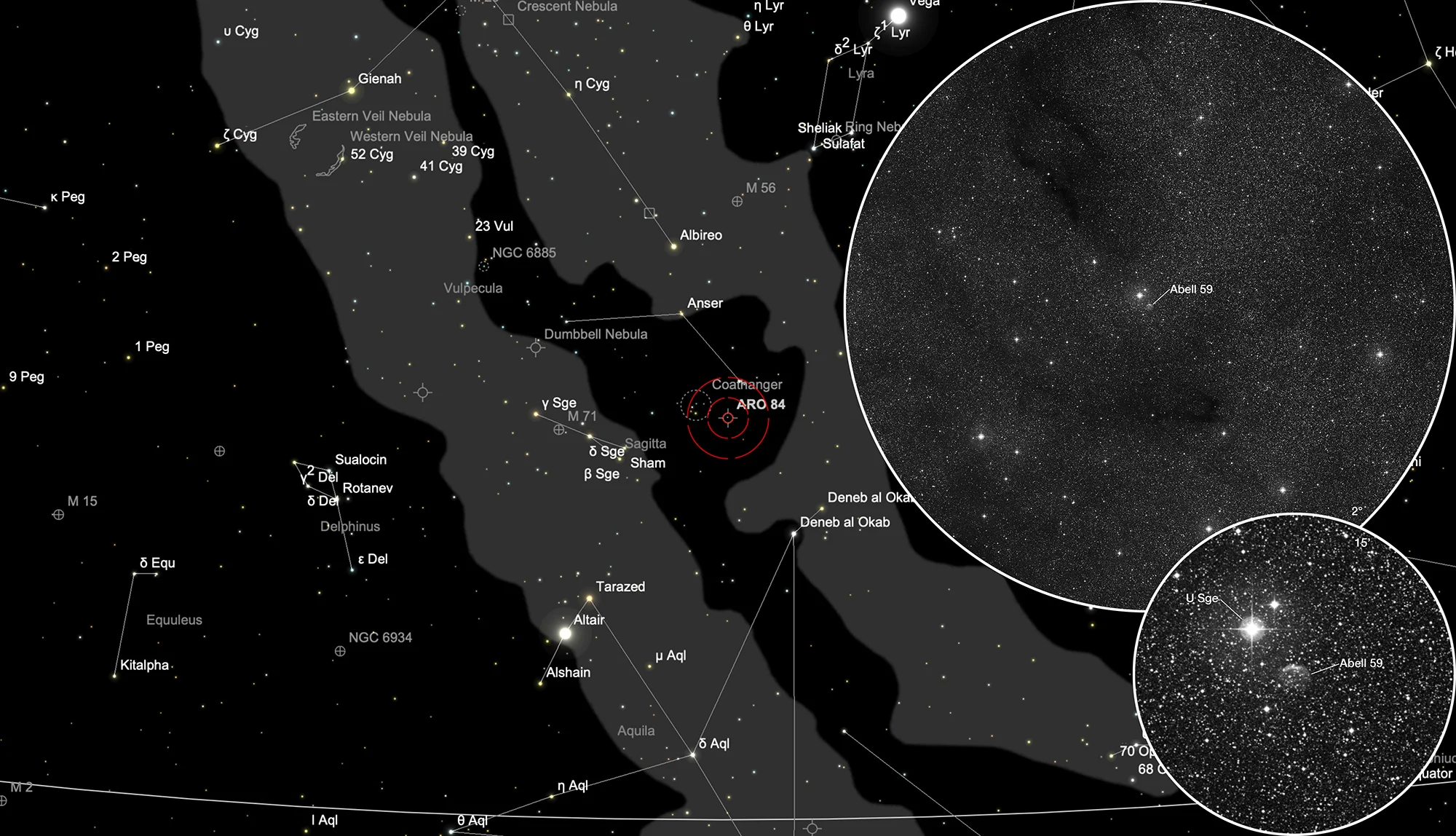
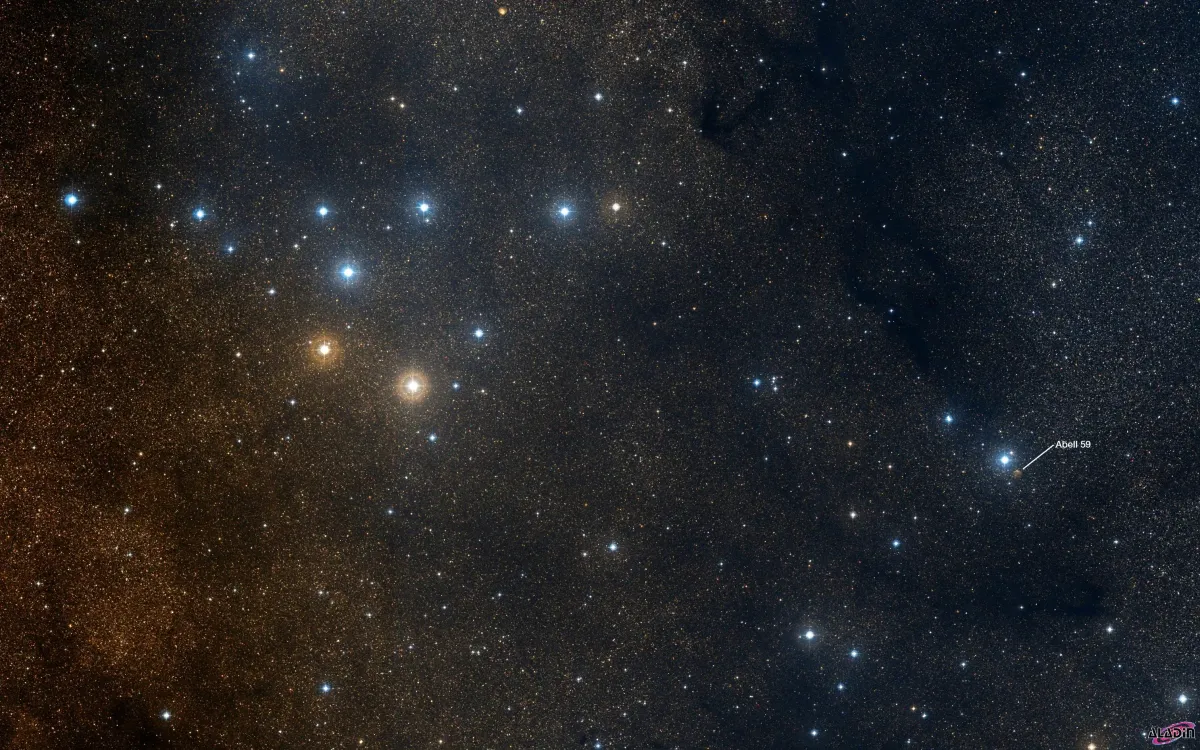
Finder Chart
The planetary nebula Abell 59 is located in the constellation Sagitta, about 1.5° west of Collinder 399. It is in opposition to the Sun on 11 July and is visible in the months March to December.