Constellation Crater (Cup)
Properties
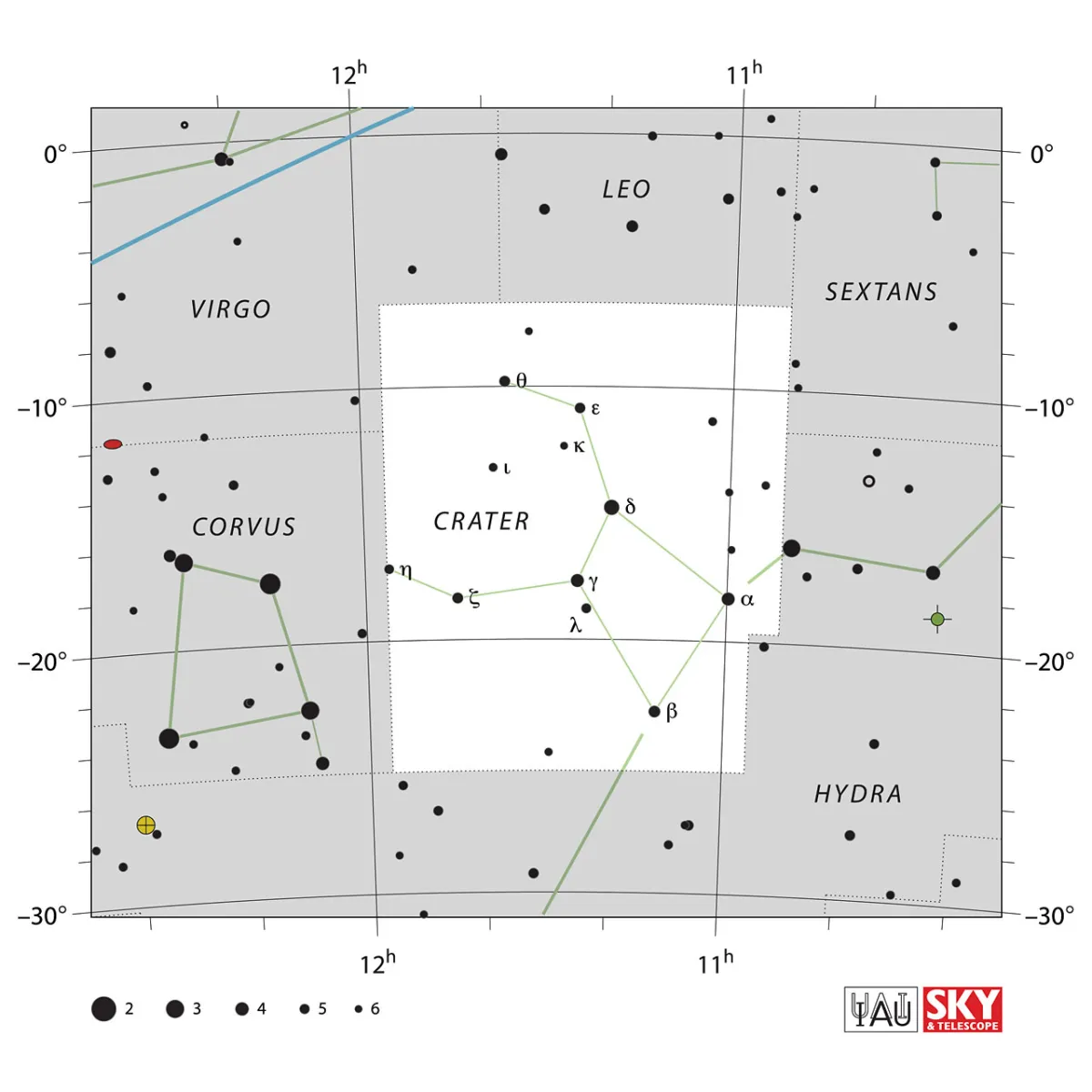
Crater is an inconspicuous constellation just west of Corvus. The three brightest stars form a right triangle with the hypotenuse in the south. The area of the constellation is 282 square degrees and the centre culminates around midnight on March 12th. [9, 15]
| α Crt | Alkes |
| IAU Name | Crater |
| IAU Genitive | Crateris |
| IAU Abbr. | Crt |
| English Name | Cup |
| Culmination at local midnight | 11 March |
| Season (Latitude +0.0°) | November … August |
| Right Ascension (J2000.0) | 10h 51m 06s … 11h 56m 24s |
| Declination (J2000.0) | -25° 11' 45" … -06° 39' 44" |
| Area | 282 deg2 |
| Neighbours (N↻) | Leo, Sex, Hya, Crv, Vir |
Catalogues
Mythology and History
Crater is an ancient constellation that represents the golden chalice of Apollo and is associated with the neighboring Corvus in the legend. In the course of the Christianization of the sky, the constellation was renamed to one of the stone water jugs of Cana, but also to the chalice of the passion of Christ, in vain. [7, 20]